Your knees are a crucial part of your body system. They get you up in the morning, keep you functioning while you move about, and keep you steady during your day-to-day activities. As valuable as these body parts are, they are prone to several unpleasant conditions, including knee pain. Knee pain is a common medical condition for which health practitioners treat patients. It can affect anyone, but it is most common in old individuals due to age.
In this guide, you will be learning about knee joint pain, some of the common causes, and proven treatments plan for knee joint pain.
What is Knee pain?
Knee pain affects the muscles and ligaments around your knee, making it difficult for you to walk comfortably. You can treat mild knee pain at home and start feeling better in days. However, there are severe cases that require the attention of a health practitioner. There are many reasons why your knee hurts, including arthritis and muscle strain.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
1. Arthritis
Arthritis is one of the most popular and top causes of knee joint pain. It is a disease that causes soreness and stiffness of the joints in the body. There are different types of arthritis such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, juvenile arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis, Spondyloarthropathies, Lupus erythematosus. Of these arthritides, osteoarthritis is the commonest cause of knee pain.
Osteoarthritis arises when there is a gradual degeneration of the cartilage in the knee joint. It is a common risk factor for knee pain among older adults. Also, constant injury, obesity, and strain can cause the cartilage to wear out quickly.
Rheumatoid arthritis can also cause bursitis. Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid happens earlier, especially when the immune system is weak. It can damage the knee by inflaming the joint and damaging the knee cartilage.
2. Torn Cartilage
The knee comprises a meniscus – a C-shaped piece of tough, rubbery cartilage. This cartilage protects the knee against impact and shock when you move or suddenly fall. In some situations, however, this cartilage may tear. Sprain and twisted ankle during a sports activity are some of the common risk factors for torn cartilage.
3. Tendonitis
This condition occurs due to the inflammation of the tendons in the knee. A tendon is a connective tissue that connects the muscle to the bones. It plays a vital role in your movement and transmits the muscle force to the bones. It is not strange to see this kind of injury in athletes during basketball or volleyball, which involves hitting the ground after a jump.
4. Obesity
The more weight you have to carry, the more challenging it is to walk. Excess weight can put pressure on the weight-bearing joints, such as the knee while sitting and standing for an extended period. Also, being obese can put you at risk of osteoarthritis due to the weakened bones around the knee joint (resulting from overuse).
5. Patellofemoral pain syndrome
This knee condition affects young adults and children. The pain usually comes from the front or behind the kneecap. You feel the sensational pain when you run, squat, cycle, or sit with your knees folded. It is also called a runner’s knee and is prevalent with people who run or jump constantly.
Specific Knee Injuries
1. Fractures
A fracture occurs when a broken bone around the knee or kneecap (patellar) occurs during a sudden shock or fall. A knee fracture is a severe condition that can affect your movement. The patellar offers cushion for the knee, but a sudden pressure or hit against a vehicle’s dashboard in a collision may affect it. People with a history of osteoporosis are also prone to a knee fracture if they misstep.
2. ACL Injury
ACL stands for the anterior cruciate ligament. This injury happens when one ligament connects the shinbone to the thighbone tears or stretches beyond its capacity. Athletes involved in sports like football and basketball, requiring sudden movements, jumps, and sudden stops, may experience ACL injury. Signs include sudden pop in the knee, limping, and swelling.
3. Bursitis
The soreness of the bursa causes bursitis in the knee joints. A bursa is a small fluid-filled sac (bursa) above the joint. Its principal function is to reduce/ friction during movement and comfort the muscles, tendons, and skin around the joint. Usually, injuries, sudden falls, overuse, and constant bending or kneeling can affect the kneecap, leading to swelling and pain. People also call this condition “soldier’s heel” or “housemaid’s knee,” while health personnel calls it “prepatellar bursitis.”
4. Strained knee muscle or ligament
You can have a strained knee muscle or ligament when you hit your knee against a hard surface. A sudden blow to the knee or shock may also cause the knee to inflame and cause redness, swelling, and intense pain.
Physical Therapy Options
Physical therapy is one of the first forms of treatment recommended by doctors. The timing of physical therapy is an essential factor in determining treatment efficiency. Patients work with a therapist to choose the right treatment plan together depending on the severity of the pain.
Discussions characterize the first session with the therapist to rebuild the strength and movement in the knees and overall legs. Also, the therapist will conduct a physical evaluation of the knee to see how it bends, moves, or straightens.
After this, the doctor will recommend some exercises at home, and sometimes, the patients will do some exercises at the treatment center. Some of the physical therapy options include:
1. Warm-up Exercise
Warm-up exercises are to prepare your legs for the activity and also reduce your chances of injury. You can ride a bike for 5 – 10 minutes or take a walk for 10 minutes. After that, do wall push-ups for five minutes.
2. Hamstring curls
This exercise is also known as the leg curls. It targets the muscles at the back of the thigh. To do this exercise, you can be in a flat position, standing position, or sitting position. Slowly bring your knees up to your butt, and hold this position as much as possible. Repeat the set three times. If it looks too easy, you can add ankle weight between 1 – 5 pounds.
3. Leg Raise
Leg raise exercise adds little or no pressure to the knee. To try this activity, be in a flat position on your back, and raise your body a bit, so it looks like you want to check your legs. Ensure you support your body with your ankles placed by your side.
Bend one knee and lift the other to the height of the bent knee. Repeat this session 10 – 15 times before switching to the other legs.
4. Prone Straight Legs
You will need to lie on your tummy with your legs straight and look straight ahead for this exercise. Tighten the muscle around your butt in one leg, and lift the other leg, holding it for 2 – 5 seconds before disengaging. Then switch to the other legs and repeat the same process. If you feel any pain, raise it lower and reduce the time.
5. Wall Squats
The difference between wall squats and ordinary squats is the wall. Stand against a wall with your feet on the ground, ensuring that your feet are shoulder-wide apart. Gently bend your knees while you keep your back and lower body against the wall. Hold this position for about 5 seconds, more or lower, depending on your strength. It is best not to bend too slowly to avoid further injuries to the knees.
Other Alternative Treatment Options
1. Medications
The doctor may recommend certain medications to relieve the strain, swelling, or stiffness in your knees. Some of these medications may be to resolve underlying conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis.
- Pain Reliever: Over-the-counter drugs for knee pain relief are ibuprofen – Pediatric Advil, Advil, Motrin IB, Nuprin, and naproxen sodium.
- Glucosamine and chondroitin: Glucosamine and chondroitin are compounds found in human cartilage. Their depletion happens due to age or overuse. However, their supplements are produced from cartilages of animals, including shellfish, cows, and pigs, because they contain anti-inflammatory substances.
- Acupuncture: Some research states that acupuncture may relieve pain and enhance steady movement in people with knee osteoarthritis for up to 12 months. In acupuncture, your doctor places fine needles in your skin at specific places (lines of energy) on your body.
2. Injections
Examples of injection doctors recommend in some cases are:
- Hyaluronic acid: Generally, the body produces hyaluronic acid in large quantities, but the natural aging processes and overuse can decrease its amounts. Aside from its supple effect on the skin, hyaluronic acid can speed up the healing process by increasing the production of blood vessels to the affected part. Doctors often inject it into the knee to reduce pain. Depending on the injury degree, you may take Injection shots for up to five or six months.
- Corticosteroids: corticosteroid drugs are a type of medication that tend to reduce inflammation in the body. Also, corticosteroids may reduce the signs of arthritis, such as swelling, redness, and pain. The corticosteroids injections may not be as effective as other types because pain relief only lasts for some months.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): PRP is a standard treatment method among athletes with a knee injury. The process involves using injections containing growth factors from the patients (platelets) to reduce pain and increase the joints and other tissues healing around the knee. These injections work better with people with a torn cartilage, ligament, or ankle sprain.
Devices and Equipment to Relieve Symptoms of Knee Pain
1. Orthotics
Orthotics help to provide stability, support, or correct joint movement. Orthotics also give enough rest for the joints, reducing the pressure that can lead to arthritis. The three types of orthotics are:
2. Braces
Doctors use braces to treat osteoarthritis around the knee. They provide adequate cushion for the knee and protect against sudden impact and shock. Specifically, they help manage the knee’s discomfort by shifting the pain from the most affected part of the knee. A brace can help you walk comfortably and cover more miles than you would without braces. They also protect the knee from further injury during sports or other tedious activities.
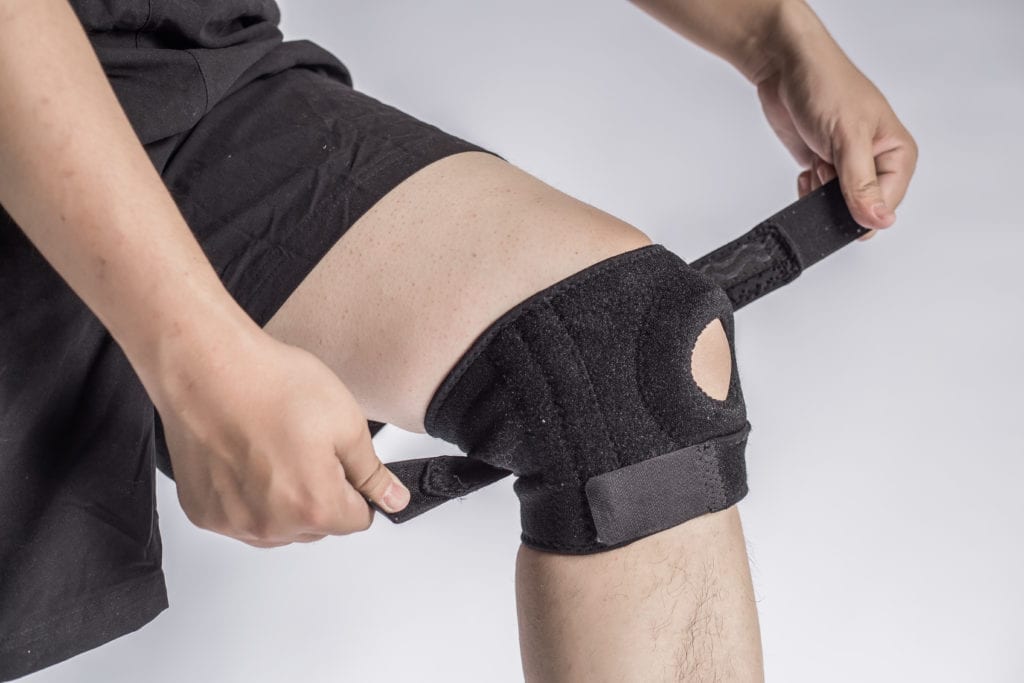
3. Dynamic orthotics
Dynamic orthotics are used to support, correct, and prevent injuries or facilitate the movement of the knee. It aligns the knee joints for accelerated motion and places them in a position that reduces stress. People who participate in sports use this treatment for knee osteoarthritis.
4. Orthopedic insoles
Orthopedic insoles help to absorb shock and impact during movement. They offer enhanced cushioning that provides stability and comfort in motion. Also, they can relieve osteoarthritic pain in the knee, foot, ankles, and hip. “Patients with arthritis can use visco-elastic insoles to absorb some of the shock transferred to the affected joint and reduce overall stress exerted on this joint.”
5. Crutches
Crutches are used after an injury to correct the deformity and accelerate motion. Doctors recommend crutches and cane to boost healing and aid movement. Besides, they help shift the body’s weight from the knee; hence, the joints carry less weight, preventing further injury or damage to the knee.
6. Thermal compresses
Thermal compresses work for random or temporary knee pain. Thermal compresses can be either cold or hot, depending on the injury type and severity. They are reusable small bags or pouches containing gelatinous products that absorb hot or coldness quickly and transfer their effect onto the affected part of the body for at least an hour. Although they may not effectively treat severe knee pain, they provide relief for a short time and permanently prevent mild pain.
Medical Procedures for Knee Joint Issues
Sometimes, patients may have to undergo surgery to correct the knee deformity and strengthen the movement. It is crucial to check the process, pros, and cons attached to each surgery type before deciding. Regardless, below are some of the surgery options available for knee pain:
1. Partial knee replacement surgery
In this surgery process, the surgeon replaces only the deformed tissues and bones around your knee with artificial metal or plastic equipment (also called prosthetics). The surgery is usually a mild one that involves small incisions; hence there is less recovery time.
2. Total knee replacement surgery
This surgical procedure requires that your surgeon cuts the faulty bone and cartilage from your kneecap, thighbone, and shinbone and replaces it with a prosthesis. Your surgeon can place the prosthesis at the lower end of your thigh bone, the upper end of your shinbone, and the backside of your kneecap.
3. Arthroscopic surgery
Arthroscopic surgery uses a tiny fiber-optic camera and a small surgical tool to repair the damaged joints around the knees by making a few cuts to repair the damaged joints. Doctors also use arthroscopy surgery to remove small pieces of broken bones or correct damaged cartilage and tendons.
Natural Remedies for Knee Joint Pain
1. Rest
Taking a rest may sound simple, but it is still one of the ways to relieve the pressure on your knees. Refrain from any activities that may trigger or worsen the joint pain. Sometimes, all a knee pain needs is a few days to rest and relieve it of excess pressure or strain.
2. Ice Pack
An iced bag of fries or peas placed on the knee can help to reduce inflammation because it covers the whole knee part. You can also put some ice in a towel and place them on the knee to reduce swelling and numbness. However, the process should not be more than 20 minutes.
3. Heat Pack
Placing a heat pack on the affected knee area may provide temporary relief for knee pain and reduce joint stiffness. Also, it relaxes the muscles and accelerates blood circulation around the damaged joints to reduce inflammation. A heat pack may work for osteoarthritis.
4. Exercise
Daily mild exercise can help to strengthen the bone structures and improve stability. Some of the activities include cycling, walking, swimming, and yoga. If you have severe knee pain, it is best to stay away from exercise, except your doctor says otherwise.
5. Ointment
A study into the effectiveness of substances containing cinnamon, ginger, sesame seed, and Matic found that they may alleviate pain when you apply it to your knee. Check out this natural solution.
Conclusion
Knee pain is a common type of pain in people of all ages and gender. Its risk factors include osteoarthritis, injury, and old age, while the treatment options available are surgery, medications, physical therapy, and simple home remedies. It will be best to see your doctor if you notice any discomfort around the knee.