Complete Guide To Patellar Tendonitis In Dogs
The knees are the most unstable body component in dogs compared to other parts, so they are relatively easy to injure. Knee problems can appear from various causes, varying from intense exercise, misplaced steps, age, and other severe circumstances. However, these injuries generally cause pain and discomfort to a dog when walking, running, or jumping.
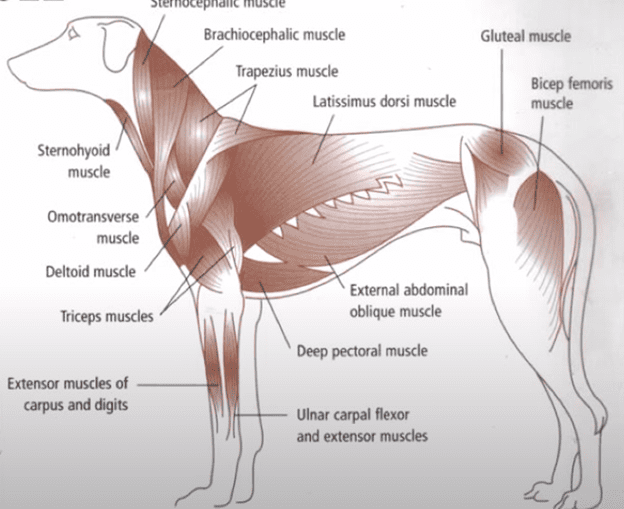
The patellar tendon is firmly attached to the tibia, and it performs the essential function of clasping the kneecap strongly. Patellar tendonitis, also known as jumper’s knee, means the inflammation of the tendons. It’s a very common problem in small dog breeds and sport dogs, and it requires timely contact with a veterinarian.
Causes Of Patellar Tendonitis In Dogs
The causes of patella tendonitis vary, but it is a purely mechanical problem. For example, in dogs, the cause of a dislocated patella can be:
1. Congenital
This is a genetic predisposition, and it typically affects dwarf dog breeds, but there are also cases of large dogs that have been affected. It is important to note that breeds that are largely affected are very agile due to their continuous physical activities.
2. Acquired
These are various knee joint injuries with fractures of the patella ligament attachment sites or rupture of the joint capsule, leading to dislocation of the patella. One of the acquired causes is a rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament since the patella can be dislocated due to instability of the knee joint.
3. Fatigue
Dogs that are not involved in exercise or intense activity (sedentary dogs) tend to develop patella tendonitis easily. These overweight dogs are usually in poor condition that results in injuries frequently when any physical exertion occurs.
4. Age
One of the factors that cause the inflammation of the tendon is the dog’s age. This is the resultant effect of the wear and tear of the bone, coupled with other nutritional deficiencies present in the dog’s diet. In addition, certain activities such as long-distance races and agility are reduced as a dog becomes older.
In conclusion, these are the four major causes of patellar tendonitis in a dog. The most common cause is the acquired injury; this is because of the recurrent physical activity exuded by the dog in running, jumping, and swings.
Patellar Tendonitis Symptoms In Dogs
Symptoms of the patella are expressed in the form of lameness and difficulty in movement. However, other symptoms of this condition are;
- Limping
- Abnormal or disorder of the natural gait of the dog
- Deformity of the thigh and lower leg
- Improper attachment of the tibial tuberosity
- Absence or shallow groove with the poorly developed medial edge
- Acute Pain
- Unwillingness to move
- Loss of appetite
- Trembling and Loneliness, etc
It is important to note that patella dislocation symptoms are divided into four degrees with their respective symptoms. The various categories are as follows;
1. First degree:
The patella can rarely be dislocated in the first degree and may not cause much pain when the dog moves. Clinically, the dog can still walk normally and actively but sometimes bends the affected region of the dislocation; there may be some extension of the knee joint, which falls back easily as the dog keeps moving.
2. Second degree:
Second-degree dislocation of the patella may also allow the dog to walk normally, but bending the limb due to the dislocation becomes painful. The patella is often dislocated and also locks into place when the knee is extended. However, the dog may restrict some of its movements, such as racing and jumping.
3. Third-degree:
In the third degree of dislocation of the patella, the dog has problems supporting the affected limb. In addition, the dog practically does not step on the sore paw; it immediately takes the wrong position when setting the patella. Therefore, the dog’s natural gait begins to change and the inflicted pain on the dog.
4. Fourth-degree:
In the fourth degree of dislocation of the patella, the dog does not use the sore paw; as a rule, the paw is constantly bent. As a result, attempts to adjust the cup may not work. This is where the dog becomes lame and restricted from movement.
NOTE: Any suspected pain during your dog’s movement, it is vital to visit the veterinary for a thorough examination with X-rays, ultrasound, or medical resonance imaging for clarity.

How To Treat Patellar Tendonitis In Dogs
There is a method for treating dislocation of the patella, especially the first-degree and second-degree dislocation without associated joint diseases on the affected limb. Often, this treatment is used for dogs with certain contraindications for specific drugs. However, the treatment involves using drugs to relieve inflammation of the knee joint and eliminate pain.
In veterinary practice, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used, such as Previcox, Loxicom, Trocoxil, Ketofen, and others. These drugs are given with a course of at least seven days before meals. Since NSAIDs (Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can cause gastrointestinal problems, it is very important to monitor your dog.
If problems appear in the form of diarrhoea or vomiting, the drug administration should be discontinued and consult a doctor. During the pain in the knee joint, compresses can be used, for example, with Dimexide diluted with water.
In any case, dislocation of the patella is a mechanical problem, so the use of physical therapy, laser therapy, or acupuncture to aid in healing makes sense when the knee joint mechanics are not severely disturbed.
Cost Of Treatment
Since the treatment of patellar tendonitis may vary from surgical to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, it is safe to cap the costs between $1,500 to $3,000 for each knee affected. However, the use of only drugs may cost for treatment may cost about $20-$50 for each month.
Therefore, it is advised that in extreme conditions of dogs, both surgical and conservative medications are used altogether to combat your dog’s discomfort. However, ensure to locate a specialized veterinarian where the treatment may be carried out properly.
Patellar Tendonitis Treatment
There are various methods of treating patellar tendonitis in dogs. However, with any treatment, early diagnosis of the patella’s dislocation is essential to avoid the irreparable consequences of the dislocation and help your pet lead an active and healthy lifestyle.

a) Surgical treatments:
Since patellar tendonitis is a mechanical problem, surgical kneecap stabilization is the preferred treatment choice. The method of patella stabilization depends on the pathological changes in the knee joint that cause it:
- With a traumatic origin of dislocation of the patella; A surgical operation is performed to eliminate the cause of the dislocation. For example, osteosynthesis is performed with a fracture of the tibial tuberosity or when the joint capsule ruptures.
- In the case of genetically determined dislocation of the patella, stabilization is carried out. Also, where there is a deformity of the thigh and lower leg, a corrective osteotomy of the thigh or lower leg bones is performed. This operation is performed after the end of the growth of the dog to avoid subsequent deformation.
- If tibial tuberosity is incorrectly located, the tuberosity is transferred to the anatomically correct position. Next, fasten the tuberosity with a knitting needle or screw.
- In the absence of a shallow groove, the groove is deepened by various surgical methods, for example, wedge-shaped plastics of the groove.
- With an excessive rotation of the lower leg, an operation such as a lateral suture is performed.
Sometimes, when carrying out surgical treatment to stabilize the patella, a combination of several techniques is required since there can be several reasons for the dislocation of the patella.
b) Braces
While most people will opt-in for the surgical treatments in most cases, there is another option – the use of braces. If the condition of the patellar tendonitis is not severe, braces are an excellent option to consider. Adopting a brace for treating the patellar helps stabilize the tendon and other structures of the bones for proper amendment.
There are two types of braces to employ depending on the height, the severity of the patellar, and breeds of dog. The rigid braces are used especially for the knee cap region, i.e., when there is a need for a more firmed binding, as it does not permit any component of the bone to move of the knee cap.
While the flexible braces are used in the knee region but, they are a minimum amount of freedom when the brace is used. Also, the flexible brace is recommended for small breeds, e.g., Pomeranians and chihuahuas, plus they are less expensive than the other type of brace.
Exercises For Patellar Tendonitis In Dogs
For dogs with patellar tendonitis, it is important to restrict intense exercise for the time indicated by your veterinarian. This could be for three weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the tendonitis and any other damage to the joints.
If a dog is known for many exercises, such a dog will be frustrated by not running and playing. However, allowing intense exercise may lead to chronic tendonitis if the area does not heal properly. Therefore, it is recommended to buying a long-lasting chew toy and teaching your dog new tricks that don’t include much physical activity will keep them busy and less bored.
To avoid obesity in your dog and ensure fitness, specific exercises that are not intense are recommended for a brief period;
- Walking a considerable length with your dog
- Moving up the stairs and returning back
- Carrying out army crawling with your dog
- Swimming or walking on an underwater treadmill
You should be able to feel all of your dog’s ribs easily and see it waist. This can be accomplished by a feeding regime as well as a little exercise. However, excess weight will make it harder for a dog to heal joints and connective tissue from injuries and make it more likely to re-injure itself later.
Natural Remedies For Patellar Tendonitis
Apart from procuring orthodox medication for the healing of the patellar tendonitis, other natural medications have proven to be very effective. These materials carry special ingredients that are well known to be anti-inflammatory; they are;
● Fish Oil:
- Due to its high content of Omega3 fatty acids, it also has a positive effect on metabolism, allergies, and inflammatory processes, for example, in the context of inflammation of the tendon.
● Turmeric:
- This natural material for centuries has been used by healers against inflammation. Its anti-inflammatory effect through its active ingredient, “curcumin,” is known to be very effective in killing bacterial. Therefore, it is mostly found in recent medications due to its vast role.
● Ice:
- Ice in the joints of his dog by establishing a bag of ice or frozen peas wrapped in a towel light around the knee. This will temporarily reduce the swelling and give your dog some pain relief.
● MSM (methylsulfonylmethane):
- This natural medication has been considered as the wonder of nature to man. The material has been applied to regions of swelling and sores, and it has been effective in combating these abnormalities. In addition, it is very applicable in pain cases due to inflammatory processes in the joints and tendons and Leishmaniasis.
● Local Heat
- Local heat is a far aged method, yet very effective in preventing patellar tendonitis. It works by applying a warm wet blanket or hot water bottle to the affected area, causes blood vasodilation, and reduces inflammation and pain.
It would help if you never treated your dog with medicines for human use without veterinary supervision. Before treatment, ensure a good diagnosis and then treat the pathology with medical treatments if necessary and with natural anti-inflammatories that help our dog relieve discomfort or pain without generating any adverse effect from the chemical drugs.
Patellar Tendonitis Prevention In Dogs
There are several methods to be incorporated into the daily routine of the dog to prevent the occurrence of patellar tendonitis, and they are as follows;
- Ensure that your dog practices light exercise regularly. This is because intense exercise, as shown above, has proven to be one of the causes of this disease. Therefore, a light activity that keeps your dog fit is to be encouraged.
- Proper stretching of the feet. This is another major cause of dog misplaced steps, which can be corrected if your dog’s feet are properly stretched. Also, this action keeps the legs active.
- Putting on knee support during sporting hours. Dressing your dogs in the proper and complete kits can serve as a way of reducing the risk of crashes and wears in the bones.
- Discontinuing High jump and landing on hard surfaces. Some of the hard surfaces, such as concretes, should be avoided. This is to avoid the pain that will come along the strong fall, which may cause a fracture of the bone.
- Proper massaging. With proper massaging of your dog can solve a future crisis. Most veterinarians carry out the service of massage when your dog has general body weakness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tendonitis in dogs is usually caused by trauma when the dog is running or jumping and injures the tendon from falling or overextending the joint. Therefore, therapeutic treatment includes using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to treat the first and second degrees of tendonitis. At the same time, surgical methods are used if the dog develops lameness with pain for several weeks.
Most dogs can be cured by transposition of the tibial roughness, trochleoplasty – a deepening of the femur block, or by duplication of the joint capsule. However, carrying out the prognosis of the degree of dislocation of the tendon before embarking on any treatment method is crucial. Also, early diagnosis of the patella’s dislocation is essential to avoid the irreparable consequences of the dislocation and help your pet lead an active and healthy lifestyle.


