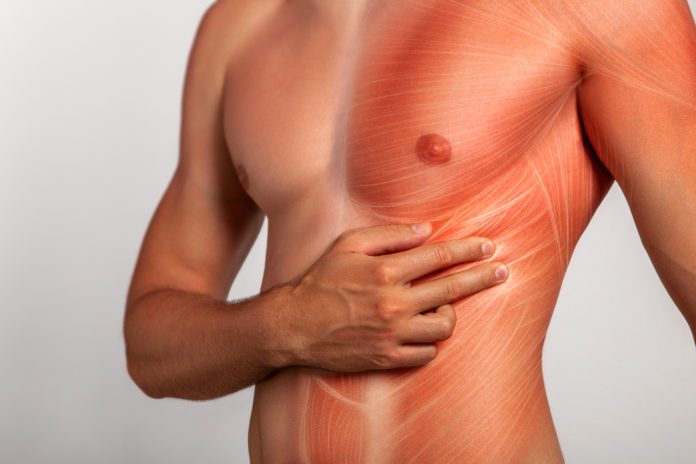
Intercostal muscle strain is an injury that affects the muscles between two or more ribs. The intercostal muscles possess different layers that are connected to the ribs. They help in building the chest wall and assist in breathing.
What is Intercostal Muscle strain?
The intercostal muscles are located between the ribs, connecting them. They aid in balancing your upper body and aid breathing. There are three intercostal muscles: the external intercostals, the internal intercostals, and the innermost intercostals.
A strain occurs when a muscle stretches, pulls, or is partially torn. A strain on any of the layers of the intercostal muscles can result in discomfort and make it difficult to breathe.
Muscle strains are the most popular cause of chest pain, about 21 to 49 percent of all musculoskeletal chest injury comes from the intercostal muscles.
There are numerous ways you can strain or pull your intercostal muscles. The muscles often get hurt while you are performing some twisting motion. Discomfort often occurs due to a sudden injury, or it can be a gradual process from performing repetitive movements.
Causes of Intercostal Muscle Strain
Below are some of the activities that can result in Intercostal muscle strain. These activities place a burden on rib muscles:
- Reaching overhead while trying to paint a ceiling.
- Heaving while twisting.
- Splitting wood.
- Intense coughing and sneezing.
- Taking part in sports like rowing, golf, tennis or baseball.
- Falling hard.
- Direct force to the ribcage, like being involved in a car accident or during sports.
- Impact force from contact sports like hockey or football.
- Twisting the torso beyond its usual span of motion.
- Twisting while lifting weights.
- Forceful twisting from playing golf or tennis.
- Forceful twisting from certain yoga positions or dance steps.
- Raising any heavy object aloft above shoulder height for a long period.
- Repetitive forceful movements, such as trying to hit a tennis ball.
A sudden increase in physical workouts can also result in intercostal muscle strain. This case often occurs when the muscles are weakened due to poor posture, hygiene, or absence of exercise.
Symptoms of Intercostal Muscle strain
Signs and symptoms of intercostal muscle strain can differ depending on the individual, but frequently, the symptoms are the same. Some of the symptoms include:
- Intense pain in the upper back and ribs.
- Intense and abrupt pain, especially if it is caused by a hit to the chest or back.
- Gradual worsening of the pain after engaging in repetitive motions such as rowing, swimming or other physical activities.
- Paralysis and tension in the muscles, resulting in discomfort and pain in the upper back.
- Rigidity in the muscles while bending or twisting the upper body.
- Intense pain while coughing, sneezing, or taking a deep breath.
- Occasional spasms of the intercostal muscles.
- Tenderness and softness in the area surrounding the ribs.
Intercostal Muscle strain Relief
Below are some ways to get relief from pains associated with intercostal muscle strain:
- Over-the-counter medication: Taking medication can help relieve pains that stem from intercostal muscle strain. If the pain is moderate or severe, you might try using anti-inflammatory pills to boost your recovery.
- Gentle Exercising and Stretching: It is important to stop whatever exercise or activities worsen your pains in the early stages. It would help if you took extra precautions to move the affected part to guard against stiffness slowly. It will be helpful to start some gentle exercises and stretches to boost your flexibility and range of motion in your thoracic region. Your stretching exercises should always be done under the supervision of a trained health professional in a bid to ensure that your injuries don’t flare up or, worse, getting new injuries. A soft tissue occupational therapist will guide you on suitable stretches for your intercostal strain.
- Heat: Applying heat to the affected parts by using a heat pack will reduce the pain resulting from cervical spasms. Heat is a cheap and beneficial form of pain relief that increases blood flow to the affected area. This helps to relax the muscles, increase range of motion and flexibility. Moreover, by increasing the circulation and blood flow throughout the area, the injuries are healed faster. It also accelerates repair and reduces the pain from the intercostal strain.
- Visit a Soft Tissue Occupational Therapist: Making an appointment with a Soft Tissue Occupational Therapist will be beneficial in treating intercostal strain. A soft tissue occupational therapist will assess to deduce the cause of the strain and then provide hands-on neuromuscular techniques such as trigger point therapy, dry needling and myofascial release to boost the functioning of the muscles, tendons, ligaments and fascia. These neuromuscular techniques help you break down fibrous adhesions, release tight muscles, and correct improper muscle functioning and postures. Soft tissue occupational therapists will also create and recommend stretching and strengthening programs to help relieve symptoms and guard against the future recurrence of intercostal strains.
Intercostal Muscle strain stretches
Below are some exercises and stretches that will aid in alleviating intercostal pain:
- Breathing Exercises: These exercises fill up the lungs with air, which expands the chest and works on the intercostal muscles. To perform this exercise, it is recommended that your back remain straight while you decide on the most favorable position – sitting or standing. Start by taking a deep breath from the bottom of the lungs. It will help you picture an image of yourself drawing breath from the diaphragm by gradually widening the abdominal muscles while inhaling, then pushing out the air from the lungs using the same muscles. Repeat these breathing exercises for 5 to 10 minutes.
- Gate Pose: A familiar yoga stance that stretches the intercostal muscles at the side of the torso. To perform the exercise, sit on comfortable padding, rise on both knees, and stretch the right leg straight to the side, with the kneecap is facing upwards and the sole firmly placed on the ground. Stretches both arms sideways. Then, twist the upper body towards the right so that the right arm can rest on the extended leg. Proceed with stretching the left arm overhead until you feel a stretch in the left ribs. Hold the stretch for a duration of 15 to 30 seconds, then repeat for the other side.
Intercostal Muscle Strain Vs. Broken Ribs
Broken Ribs
Broken ribs or rib fracture occurs as a result of cracking of one of the bones in the rib cage. It can also happen from a fall or accident. Intense and prolonged coughing and sports that entail repetitive movements such as golf can also cause rib fractures.
Symptoms
Symptoms of broken ribs include:
- Feelings of pain in the chest area when taking a deep breath.
- Pain when pushing down on the injured area.
- Feelings of discomfort while bending or twisting the body.
- Shortness of breath.
- Tenderness in the affected area.
- Bruises.
- Intense coughing.
- Feeling or hearing a crack sound.
- Swelling and inflammation in the affected area.
- Feeling of breathlessness.
- Sharp stabbing sensation in the rib region.
Treatment
Rest
Ice pack
Compression
Heat therapy
Analgesics
Use of NSAIDs
Intercostal Muscle strain
Intercostal muscle strain is an injury that affects the muscles between two or more ribs.
Symptoms
- Intense pain in the upper back and ribs.
- Intense and abrupt pain, especially if it is caused by a hit to the chest or back.
- Gradual worsening of the pain after engaging in repetitive motions such as rowing, swimming or other physical activities.
Treatment
Ice therapy
Heat therapy
Rest
Use of pain relievers
Use of splints if breathing is painful.
Physical therapy
Intercostal Muscle strain Treatment
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can be used to treat Intercostal muscle strain through numerous types of exercises and stretches. These exercises and stretches aid in strengthening the intercostal muscles. The exercises might include:
- Strengthening exercises.
- Stretching exercises.
- Foam roller stretches.
- Deep breathing exercises.
If taking a breath becomes difficult, deep breathing exercises are often recommended to enhance a person’s shallow breathing since long-term shallow breathing can result in pneumonia. A person suffering from intercostal muscle strain should not attempt any stretching exercise unless the direction of a physical therapist or other health care professionals.
Acupuncture: Unlike other treatments, Acupuncture specifically targets the muscles and the affected areas. This can directly treat the problem, not just address the symptoms. An Acupuncture treatment starts by identifying a patient’s patterns of holding pressure within the muscle that leads to the strain. The needles are then inserted into the meridian pathways to stimulate the body into reconfiguring its balance.
Surgery: Often, intercostal muscle strains do not require surgery to heal. However, if the muscle is completely ruptured, the patient might be needing surgery.
Braces and compression sleeve: Your doctor might recommend the use of braces to support your Achilles tendon and prevent the injuries from happening again.
Exercises for Intercostal Muscle strain
- Gate Pose: A familiar yoga stance that stretches the intercostal muscles at the side of the torso. To perform the exercise, sit on comfortable padding, rise on both knees, and stretch the right leg straight to the side, with the kneecap facing upwards and the sole firmly placed on the ground. Stretches both arms sideways. Then, twist the upper body towards the right so that the right arm can rest on the extended leg. Proceed with stretching the left arm overhead until you feel a stretch in the left ribs. Hold the stretch for a duration of 15 to 30 seconds, then repeat for the other side.
- Breathing Exercises: These exercises fill up the lungs with air, which expands the chest and works on the intercostal muscles. To perform this exercise, it is recommended that your back remain straight while you decide on the most favorable position – sitting or standing. Start by taking a deep breath from the bottom of the lungs. It will help you picture an image of yourself drawing breath from the diaphragm by gradually widening the abdominal muscles while inhaling, then pushing out the air from the lungs using the same muscles. Repeat these breathing exercises for 5 to 10 minutes.
- Forward Stretch: These exercises are used to stretch the intercostal muscles to the direction of the back of the torso. Sit on the floor while placing your left leg straight in front of your body while keeping the right leg bent so that the sole makes contact with the knee. Then, lean forward as far as you can over the right leg, rotating the torso slightly, and place both palms on the floor, if possible. You should feel a stretch in the back of the intercostal muscles on the left side. Maintain the stretch for 15 to 30 seconds. Then repeat on the other side.
Natural Remedies for Intercostal Muscle strain
Below are some of the natural remedies for intercostal muscle strain:
- Over-the-counter Painkillers: Before you consult your doctor, you can take over-the-counter anti-inflammatories like ibuprofen (Advil) or naproxen (Aleve) or some simple pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol). Read the directions to know how to use the pills.
- Heat and Ice Therapy: Ice therapy can help alleviate your discomfort as lessen the inflammation of the muscles. Place an ice pack on the affected area for 20 minutes at a time. You can repeat it several times daily for the first two days. You can make use of an ice bag, a cold gel pack, a plastic bag filled with ice and wrapped in a towel. A bag of frozen veggies would do the trick as well. After the first two days, you may begin heat therapy on the injured ribs. Heat can help you relax the muscles so you can do your physical therapy. You can apply heat for 20 minutes at a time with a heating pad or a warm damp towel.
- Epsom Salt soaks: As a part of the heat therapy, you should consider taking a warm bath with magnesium sulfate (Epsom salts) added. You can get Epsom salts from any local drug store or online at Amazon.com. Add about 2 cups to your bath and soak in it for 15 minutes or more. The dissolved minerals are absorbed through your skin, and magnesium levels in your blood might increase due to this. Magnesium is an important mineral for muscle functions. Although the little amount of magnesium absorbed into your body from the bath is unlikely to help your strained muscles, the hot bath can help you relax your muscles.
- Breathing Exercises: Breathing while suffering from intercostal muscle strains can be painful. However, taking shallow breaths – instead of full, deep breaths – can lead to pneumonia. Deep breathing exercises can also be used as a type of meditation to reduce stress. Try to take deep breaths once in a while.
- Natural Ointment: You can try Joint Mud to get some mobility and relieve pain. This will make the healing process easier to deal with.
Prevention of Intercostal Muscle strain
Prevention of intercostal muscle strain entails warming up and stretching before starting strenuous and intense exercises. It is also not to overexert yourself when working out or playing sports. Strengthening exercises also help prevent intercostal muscle strain.
Conclusion
Intercostal muscle strains can take a long period to heal, which may be frustrating. If your strain is a severe case, your doctor might have to give you lidocaine and corticosteroids to lessen the discomfort and swelling.
A rib stress fracture constantly accompanies intercostal muscle strains. However, even if you do suffer from a stress fracture, your treatment won’t differ by much. Follow your therapy programs, do breathing exercises, and your injuries will heal in no time at all.
To prevent future recurrence of muscle strains, always warm up before starting any exercise or sporting activities. Do not overexert your body to perform activities that it is not used to.