Hormones play significant roles in maintaining your physical, mental, and emotional health. They regulate and control several physiological functions- height, weight, temperature, mood, appetite, sleep, amongst others.

Introduction
Hormones are chemical substances produced by endocrine glands. They initiate, sustain or stop various processes and functions in your body. They act as messengers- communicating with your nervous system, determining what is done and when, and sending warnings when something is wrong. Some of these functions include growth, temperature, appetite, metabolism, sleep cycles, heart rate, mood, and reproductive function.
However, for them to act optimally, they need to be produced and released in the right amounts. Overproduction or underproduction results in imbalance and can result in several disorders, which may also be life-threatening.
Endocrine glands- are tissues and organs that make up the endocrine system. They include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, adrenal glands, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. They are ductless glands, that is, they release the hormones they produce directly into the blood.
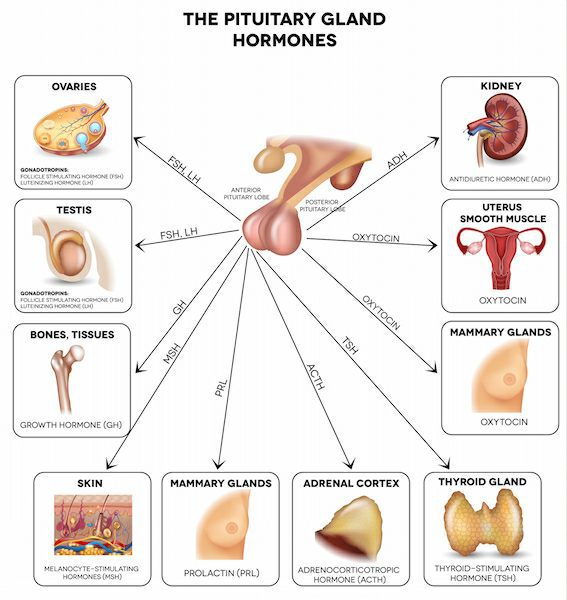
Hormonal imbalance occurs when these hormones are in either too much or too little within the bloodstream. Even the minutest of changes in levels can cause adverse effects. When this happens, you may feel or notice some symptoms including weight changes, appetite changes, temperature changes, mood swings, insomnia, fatigue, and hair changes. In recent times, hormonal imbalances have become an increasingly common medical disorder.
Causes of Hormonal Imbalance
It is normal to experience natural episodes of hormonal imbalance at some point in your life. However, it may have an underlying cause (or causes). These causes include:
- When the endocrine gland is not functioning properly. This can be any of the organs in the endocrine system. Unfortunately, the effect of a poorly functioning gland can be widespread. That is, the overproduction or underproduction of a hormone can affect the functioning of other glands and cause more damage. Hormones are interdependent, the release of one may result in the production or inhibition of another, thus an imbalance could have a ripple effect.
- Medical conditions. Some medical conditions may affect the function of a gland or affect the levels of a hormone in the blood, thus resulting in hormonal imbalance.
- Lifestyle habits. Nutrition (or diet), sleep, and physical activity can influence the production, release, and use of hormones in the body.
- Environmental factors. Exposure to certain agents in the environment without the body can affect how hormones are produced or used within the body.

These causes are further listed below:
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid)
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)
- Diabetes (Type 1 and 2)
- Hormonal replacement therapy
- Pituitary tumors
- Tumors of endocrine glands – benign or malignant (cancer)
- Chronic or high levels of stress
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypoglycemia
- Poor diet
- Phytoestrogens (found in soy products)
- Obesity or being overweight
- Medications e.g. steroids, birth control pills
- Cushing’s syndrome (levels of cortisol and aldosterone are high)
- Addison’s disease (levels of cortisol and aldosterone are low)
- Certain infections and allergic reactions
- Injury or trauma to the endocrine gland
- Iodine deficiency (goiter- affects thyroid gland)
- Cancer treatments- chemotherapy, radiation therapy
- Exposure to pollutants, toxins, and other chemical substances that alter endocrine function
- Hereditary and congenital disorders such as Turner syndrome, hereditary pancreatitis, congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Eating disorders, e.g. Prader-Willi syndrome
- Menopause
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
- Hypogonadism
- Anorexia
Symptoms
The symptoms of hormonal imbalance depend on what endocrine gland and/or hormone are affected. However, since hormones are interrelated in production and function, their symptoms may be similar. They include:
- Fatigue
- Anxiety, nervousness, and irritability
- Weight changes (weight gain, weight loss)
- Digestive issues-diarrhea, constipation, nausea, and bloating
- Changes in blood pressure- hypotension or hypertension
- Changes in heart rate- bradycardia (decreased heart rate), tachycardia (increased heart rate)
- Cold or heat intolerance
- Increased sweating
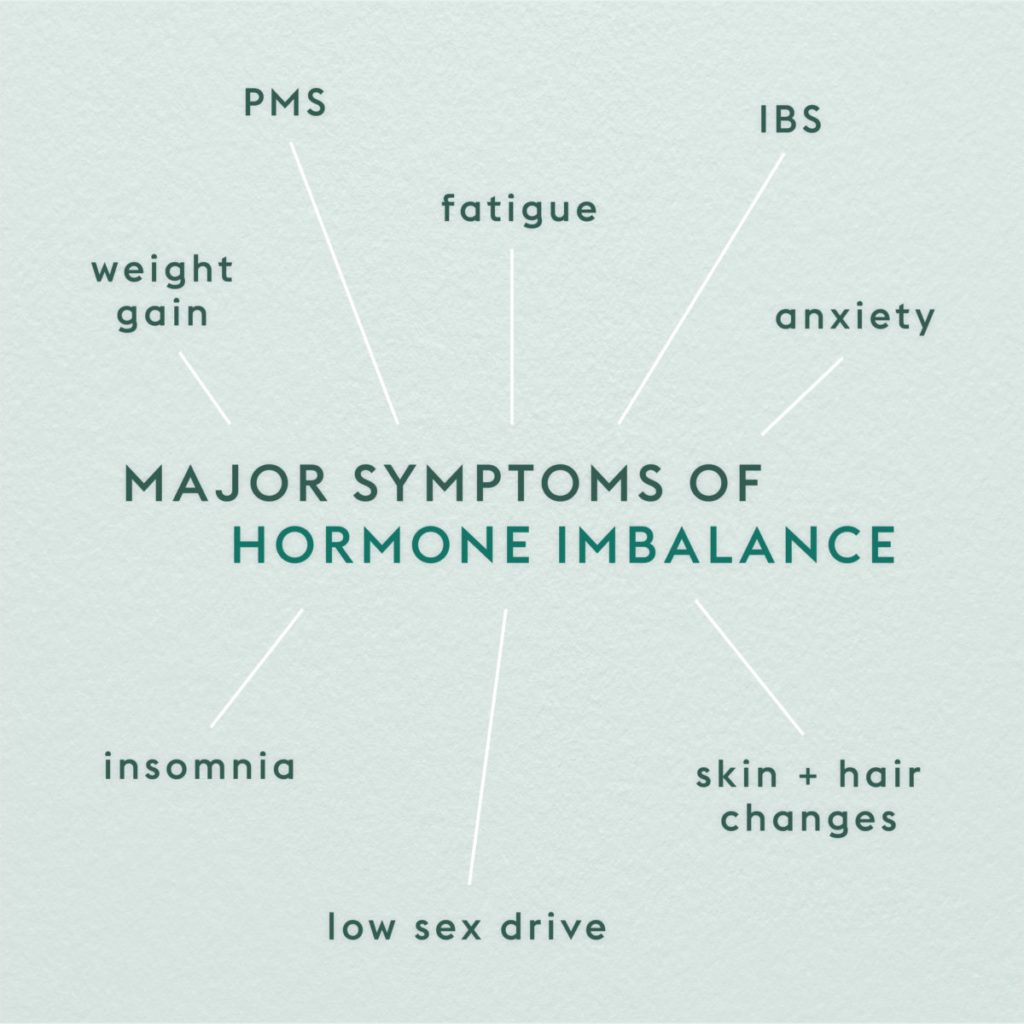
- Sleeping difficulties- insomnia
- Polydipsia (excessive thirst)
- Polyphagia (excessive hunger)
- Blurred vision
- Hair changes- hirsutism (excessive hair on the face, chin, chest, etc. in women), dry hair, thinning hair, and hair loss on the head, eyebrows, etc.
- Skin changes- acne, skin tags, dry skin, darkening of the skin
- Brittle fingernails
- Muscle weakness
- Joint and muscle pain and cramps
- Low sex drive or libido
- Changes in reproductive function and infertility- erectile dysfunction, gynecomastia (development of breasts in men), irregular periods, painful periods, heavy menstrual bleeding, vaginal dryness, painful sex, hot flashes, and mood swings.

- Changes in appearance- puffy face, hands, and feet, moon (swollen and rounded) face.
- Difficulty in balance and coordination
- Depression
- Anemia
Complications of Untreated Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalance, when left untreated can result in many other serious medical conditions. These include:
- Type 1 and type 2 diabetes
- Diabetes insipidus
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Cardiovascular diseases – heart attack. stroke
- Kidney failure and damage
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Neuropathy
- Cancers-breast cancer, endometrial cancer
- Loss of muscle mass
- Osteoporosis
- Goiter
- Sexual dysfunction
- Infertility
- Urinary incontinence
- Depression
- Sleep apnea
Natural Ways To Balance Hormones
There are natural ways to improve your hormones production and function and keep your body fit and healthy. The following are natural ways to balance your hormones:

Diet
This refers to all of the food and drinks you consume (and don’t consume) that may boost your hormonal health. This involves:
- Consuming more protein:
- Protein is essential to your diet. Having an adequate amount of protein provides your body with essential amino acids. These amino acids cannot be produced by your body and are significant to your body’s normal functioning. Proteins help build new and repair damaged tissues, including the muscles, bones, and skin.
- Previous studies show that consuming more protein reduces levels of ghrelin (the hunger hormone) and suppresses appetite. Also, a high-protein meal stimulates the production of GLP-1 and PYY- hormones that make you feel full so you don’t eat much.
- Increasing your protein intake also increases your metabolism and helps you burn fat more. To help balance your hormones, it is recommended you consume at least 20-30 grams of protein per meal.

- Consuming a high-fiber diet:
- Fiber is important in your diet. Fiber (soluble and insoluble) increases insulin sensitivity and stimulates the production of hormones like GLP-1, PYY, and leptin. They also helped to reduce appetite and avoid overeating.
- Avoiding sugar and refined carbs:
- Both have been linked to many health issues, including obesity, diabetes, heart disease, etc. Cutting down on the intake of sugar and refined carbs can help balance hormones and lower the risk of developing linked medical problems. Fructose makes up at least fifty percent of most types of sugar. It is present in both natural and refined, processed sugars. Research shows that fructose plays a role in increased insulin levels and insulin resistance. This is peculiar to overweight and obese persons with prediabetes or diabetes. Hence, avoiding sugar and refined carbs altogether is important to keep insulin levels in check and increase insulin sensitivity.
- Consuming healthy fats:
- Adding high-quality natural fats to your diet can help balance your hormones. Polyunsaturated fats help regulate your appetite, prevent overeating, and lower your risk for obesity. Examples include omega-3 and omega-6 foods. They stimulate the production of leptin, a hormone that inhibits hunger and regulates your weight. Low intake of healthy fats equals low leptin levels, causing you to overeat and gain weight. Healthy fats also stimulate the release of GLP-1, cholecystokinin, and PYY- hormones that make you feel full.
- In addition, medium-chain triglycerides (MCT) are healthy fats that the liver uses up directly as energy. They help reduce your appetite and prevent overeating. MCTs also help reduce your body’s resistance to insulin, especially in overweight and obese people, and people with diabetes. Foods with MCTs include human breast milk, coconut oil, cow’s milk, goat’s milk, palm oil, and dried coconut.
- Other healthy fats are monounsaturated fats and dairy fats. These fats increase insulin sensitivity in persons with prediabetes, diabetes, and elevated triglycerides. Monounsaturated fats are found in olive oil, avocado, canola oils, and peanut oil. Unhealthy fats such as trans fats promote your risk for obesity and insulin resistance, hence, they should be avoided.
- Avoiding overeating and undereating:
- How you eat is linked to your weight. Eating too little or too much can cause hormonal imbalances that will result in weight problems. Research shows that eating too much increases insulin levels and insulin resistance, especially in insulin-resistant overweight and obese people.
- Undereating or too low-calorie intake can increase the levels of cortisol “the stress hormone” which in turn can make you gain weight and reduce insulin sensitivity. Eating healthy and in the right amounts help to balance your hormones.
- Adding green tea to your diet:
- Drinking green tea has numerous benefits. It contains an antioxidant, “epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)” and helps boost your metabolism. It also helps lower insulin levels and increases insulin sensitivity in both healthy people and people with conditions like obesity and diabetes.
- Consuming probiotics and fermented foods:
- Probiotics help increase the number of good bacteria you have in your gut. They make it easier for your digestive system to digest food. In balancing hormones, consuming probiotics can restore estrobolome, a bacteria concerned with metabolizing estrogen. Hence, it corrects estrogen imbalance. Probiotics also reduce the effects of stress on the hypothalamic-pituitary axis and help treat depression and anxiety. Eating fermented foods such as cider, miso, tempeh, sauerkraut, and kimchi can also help regulate gut bacteria.
Exercise and physical activity
Regular exercise and physical activity boost your hormonal health. It helps lower the amounts of insulin in your blood and increases your cells’ sensitivity to insulin. Your cells need insulin to take up sugar and amino acids for energy. When your insulin levels are high, you have a higher risk for diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. Unfortunately, these medical conditions reduce how your body cells respond to insulin.
Regular exercise also helps increase the levels of hormones that boost muscle health and metabolism. Muscle-maintaining hormones include growth hormone, DHEA, testosterone, and IGF-1. Adiponectin is a hormone that reduces inflammation and regulates metabolism.
Exercise and physical activity that you can do include aerobic exercise or cardio like brisk walking, swimming, cycling, and sports (basketball, football, baseball, etc.). Others are strength training and endurance exercises.

Get Quality Sleep
Diet and exercise are good and yield results. However, without high-quality sleep, your health will suffer. Unfortunately, busy schedules rid us of good, night sleep and this can cause hormonal imbalances. Poor sleep results in hormonal imbalances of insulin, cortisol, growth hormone, leptin, and ghrelin. According to a study, poor sleep led to an increase in the hunger hormone “ghrelin” and reduced levels of leptin, a hormone that suppresses hunger and makes you feel full.
A good night’s sleep boosts your glucose metabolism, increases the release of growth hormones and leptin levels in the body. Not only should you sleep for at least 7-8 hours, ensure it is quality sleep to maintain optimal hormonal balance.
Reduce your exposure to light at night. Blue light from devices such as cell phones, laptops, light bulbs, etc. can disturb our sleep cycle. This is because your body perceives this blue light as daylight and responds to it as it would if it were daytime. In other words, it confuses your body and suppresses the release of melatonin, which disrupts several functions. Thus, reducing your exposure to light at night can help you have a good sleep and balance your hormones.
Manage stress
Two hormones-cortisol and adrenaline (also known as epinephrine) are majorly influenced by stress. Cortisol is the hormone that helps your body deal with stress over time and is called the “stress hormone”. Adrenaline, also known as the “fight-or-flight hormone” is released when your body is faced with dangerous, stressful, emergent, or exciting situations. It provides your body with lots of energy to take quick and vigorous actions.
Normal day-to-day activities especially busy and overwhelming ones can increase the levels of these two hormones. In high concentrations, they can result in excessive hunger, obesity, mood swings, anxiety, and heart problems. Learning to manage stress is thus, important. Techniques such as massage, yoga, meditation, and listening to music may help reduce stress and its effects.
Quit smoking
Smoking tobacco can result in hormonal shifts. It may trigger the release of pituitary hormones, disrupt levels of thyroid hormone, and increase levels of cortisol.
Eliminate alcohol
While moderate consumption of alcohol may be healthy, some research shows that even these small-moderate amounts of alcohol can alter hormone levels in men. Drinking alcohol can result in changes in testosterone levels and reduce sperm quality. Hence, staying away completely from alcohol is advised for men with hormonal issues.
Conclusion
Hormones play important roles in maintaining your health. To do so, they need to be the right amounts as any slight change in their levels can alter several functions. There are natural ways to balance your hormones and these include lifestyle modifications in your diet, exercise, sleep, and stress management.
Sources:
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/balance-hormones
https://www.parsleyhealth.com/blog/hormonal-imbalance-symptoms/


