Disclaimer: Please consult with a physician first before making any modifications. High blood pressure can be dangerous and should be carefully assessed by a licensed physician. Nothing mentioned in this post is meant to replace or modify licensed medical advice. Please check with your physician if some of these tips might be beneficial for you before making any changes.
Blood pressure is the measure of the force of pumped blood against the walls of the blood vessels. Your heart pumps blood to all the parts of your body. This blood flows through blood vessels known as arteries. As the blood flows, it exerts a force on these walls.

When your doctor or health professional checks your blood pressure, it could fall within the normal or abnormal range. Usually, the abnormal range is termed high blood pressure. A blood pressure reading is written with a top number over a bottom number. The top number is referred to as the systolic, and the bottom number is diastolic.
Systolic pressure is the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats. Diastolic pressure is the pressure in your arteries between beats. Blood pressure readings are summarized below:
| Systolic (mmHg) | Diastolic (mmHg) | |
| Normal | less than 120 (<120) | Less than 80 (<80) |
| Elevated blood pressure (prehypertension) | 120-129 | Less than 80 (<80) |
| Stage 1 high blood pressure (hypertension) | 130-139 | 80-89 |
| Stage 2 high blood pressure (hypertension) | Equals to or greater than 140 (≥140) | Equals to or greater than 90 (≥90) |
| Hypertensive crisis | Over 180 (>180) | Over 120 (>120) |
Hypertensive crisis requires emergency care.
What is high blood pressure?
High blood pressure is when your blood pressure measurement is at unhealthy high levels. When your blood pressure reading has a systolic above 120 and a diastolic above 80, you have high blood pressure.
Blood pressure depends on how much blood is pumped and the resistance of the blood vessels against the blood. When your blood vessels (arteries) are narrow, the amount of resistance is higher. Hence, narrower arteries result in increased resistance and then increased blood pressure.
When the blood pressure is high for the long term, it can cause serious health issues. These include heart failure, kidney disease, stroke, vision loss and many more.
Causes of high blood pressure
There are two types of high blood pressure.
Primary/Essential hypertension
The exact causes of high blood pressure are unknown. Primary or essential hypertension is a type the develops slowly over time.
Secondary hypertension
This type of high blood pressure is caused by an underlying condition. The blood pressure shoots up suddenly and has readings higher than those of primary hypertension.
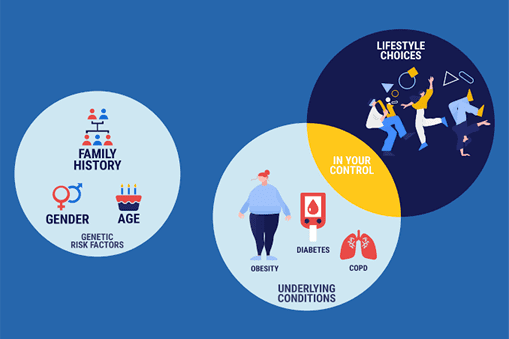
Several factors increase a person’s risk of developing high blood pressure. They include:
- Older age
- Genetics
- Family history of high blood pressure
- Obesity
- High alcohol consumption
- High salt intake
- Smoking
- Medical conditions such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease, heart diseases, thyroid disorders, etc.
- Stress
- Pregnancy
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Sleep apnea
- Race (African-Americans)
- Certain medications such as birth control pills, over-the-counter (OTC) pain relief drugs, decongestants, etc.
- Illegal drugs such as cocaine.
Signs and symptoms of high blood pressure
Usually, people with high blood pressure do not experience symptoms. This is why high blood pressure (or hypertension) is called the “silent killer”. However, when a person’s blood pressure reaches a reading of 180/120 mmHg and above, it becomes a hypertensive crisis. The person may experience:
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision
- Nose bleeds
- Heart palpitations
- Breathlessness
Symptoms of high blood pressure in women
Hormonal influences put women at risk of developing high blood pressure. This may occur during any of pregnancy, use of contraceptive (birth control pills) and menopause.
High blood pressure in pregnancy is a risk factor and maybe a sign of pre-eclampsia. Pre-eclampsia is a medical emergency that may be fatal for both mother and the baby in the womb. Symptoms that a pregnant woman may experience include:
- Severe headache
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision or visual disturbances
- Oedema or swelling in the face, hands, and feet
- Upper abdominal pain (just below the ribs)
- Nausea and vomiting
Symptoms of high blood pressure in teens
While high blood pressure is most common in adults, teenagers can develop it too. This may due to obesity, an underlying medical condition or certain medications. Medical conditions that result in high blood pressure include:
- Kidney disease
- Type 2 diabetes
- Lung problems
- Endocrine diseases
- Heart and vascular problems
- Neurological diseases
A teenager with high blood pressure can experience the following:
- Headaches
- Blurry vision
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Fluttering heartbeats/ heart palpitations
- Nosebleeds
Symptoms of high blood pressure in children
High blood pressure can also be seen in children. Conditions that may cause high blood pressure include:
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Tumors
- Heart diseases
- Kidney problems
- Cushing’s syndrome
- Thyroid disorders, amongst others.
Symptoms if experienced may include:
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Nosebleeds
- Heart palpitations
- Vomiting
Symptoms of high blood pressure in babies
Babies often have blood pressure as a result of underlying health conditions such as heart disease, lung problems, and kidney diseases. The following may occur:
- Failure to thrive
- Seizures
- Irritability
- Vomiting
- Lethargy
- Difficulty in breathing
Consequences of untreated high blood pressure
Persistent high blood pressure can cause damage to your blood vessels and vital organs. When left untreated, the damage is greater. The following are consequences of untreated high blood pressure:
Heart attack. As the force of the blood flowing through your arteries increases, it damages your blood vessels. This can lead to scarring and the collection of plaques within the arteries. prolonged injury can cause the vessels to get narrower and finally get blocked. When the artery supplying blood to the heart muscle is blocked, the result is a heart attack.
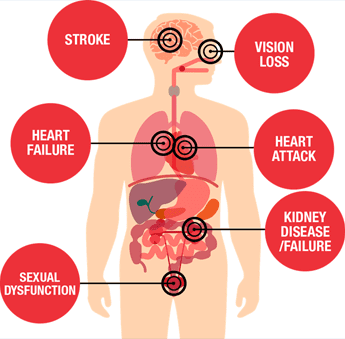
Stroke. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can cause other blood vessels to rupture or get blocked. this is due to the increased pressure which can cause tears and scars. A stroke occurs when the blood vessels to and within the brain rupture or are blocked by clots or plaques.
Aneurysm. High blood pressure can create weak spots in arteries. these areas get filled with blood and bulge out of the wall of the artery. This is then called an aneurysm. Over time, these aneurysms get weaker, rupture and leak into surrounding tissues, and can cause a stroke.
Heart failure. High blood pressure gives your heart more work to do. As a result, the muscles of the heart get bigger (hypertrophied) and can not pump blood efficiently. This is referred to as heart failure.
Kidney problems. Uncontrolled high blood pressure causes the blood vessels in the kidneys to weaken and get narrower. Hence, the kidney can no longer remove waste and excess fluid,
Eye problems. High blood pressure can cause the blood vessels in your eyes to grow thicker, weaker, and rupture. When they do, there is bleeding within the eye, fluid accumulation, or blurred vision. With time, it could lead to vision loss or blindness.
Memory and cognitive problems. Untreated high blood pressure can lead to impairment in thinking, learning, and memory.
Erectile dysfunction. High blood pressure affects the blood supply to the penis. Inadequate blood flow makes it difficult to achieve and maintain erection and ejaculate. It also reduces sexual drive in men.
Metabolic syndrome. These are a group of disorders that reveal your likelihood of developing diabetes, heart disease or stroke. These disorders include increased waist circumference, high insulin levels, decreased high-density lipoprotein (HDL), cholesterol, high triglycerides and high blood pressure.
Peripheral artery disease. High blood pressure can cause plaques to form with peripheral arteries. This reduces the amount of blood that gets to the tissues in your buttocks and lower limbs. These areas may become painful, numb, and feel heavy.
Treatment of high blood pressure
Medications
High blood pressure is controlled using different classes of drugs. They include:
- Diuretics- helps your kidneys excrete excess sodium/salt and water out of the body
- Beta-blockers- slows down the heartbeat and reducing cardiac workload and output
- Alpha-blockers -reduce arterial resistance
- ACE Inhibitors- inhibits the production of angiotensin
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)- blocks the effects of angiotensin
- Calcium channel blockers- prevents the influx of calcium into the smooth muscle of the heart and arteries.
- Central Agonists- decrease blood vessels’ ability to tense up and contract.
- Alpha-2-receptor agonists- decrease the activity of the sympathetic nervous system.
- Vasodilators- relaxes the muscular walls of blood vessels and cause them to dilate.
- Peripheral adrenergic inhibitors- block neurotransmitters in the brain.
Lifestyle modifications
Lifestyle modifications are majorly preventive measures for high-risk populations- older populations, those genetically and environmentally predisposed. However, they are also critically essential in controlling high blood pressure. Medications help but may not do so much especially in patients who:
- are overweight or obese
- actively smoke
- drink alcohol in excess
- live sedentary lifestyles or perform little activity
- are exposed to stressful conditions
- consume high levels of dietary sodium and low levels of dietary potassium.
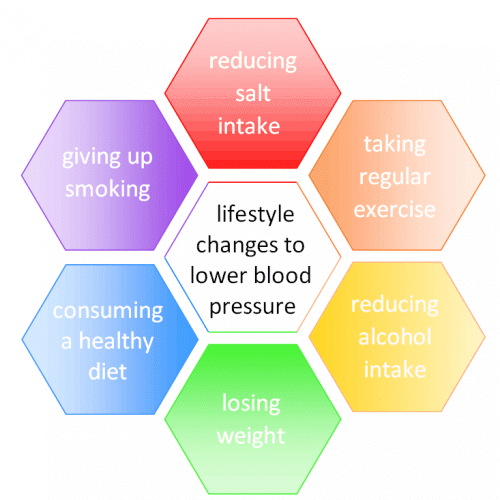
The following are lifestyle modifications you can make to control your blood pressure:
Eat a healthy diet.
The recommended eating plan is known as the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. The DASH diet includes foods that are rich in potassium, calcium and magnesium. This implies eating a diet rich in whole grains. fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products.
Foods that are high in sodium, saturated fats, cholesterol and added sugars are cut out. It is designed to help prevent and lower high blood pressure by up to 11 mmHg. To ensure you eat healthily, watch your eating habits. Keeping a food diary can help you track what you eat, how much, when and why.

Increase potassium intake
Potassium act as antihypertensives and can lessen the effects of sodium on blood pressure. Potassium supplements can be taken, however, the best options include food such as fresh fruits and vegetables. Increased intake of dietary potassium helps reduce the risk of stroke.
Increase intake of other minerals
Minerals such as calcium and magnesium have been proven to help reduce blood pressure levels. Studies showed that calcium played a significant role in reducing blood pressure by 1.44/0.84mmHg. Magnesium showed a similar effect with an increase in dose.
Cut back on sodium
Cutting back on your sodium intake can boost your heart health. Adding low sodium intake to your DASH diet has been shown to efficiently reduce blood pressure. In persons with high blood pressure, reduction in sodium intake can reduce blood pressure by about 5 to 6mmHg.
General advice is to limit your sodium intake to 2,300 milligrams (mg) a day or less. However, the ideal sodium intake for most adults is 1500mg a day or less. To cut back on your sodium intake, do the following:
- Go for low-sodium foods and beverages when you shop. Go through labels to make the right choices.
- Reduce intake of processed foods. Processed foods account for 75% of sodium intake as only a few natural foods have sodium.
- Make use of herbs and natural spices when cooking. Instead of salt, use substitutes like garlic, lemon juice (zest), onion, dill, etc.
Quit smoking
Generally, smokers have been found to have higher daytime ambulatory BP. Smoking cigarettes raises your blood pressure for long periods each time you do so. It increases sympathetic outflow and insulin resistance.
Avoiding tobacco helps your blood pressure return to normal levels. Quitting altogether prevents heart diseases, lung problems and improves symptoms of kidney disease. People with high blood pressure who quit smoking live longer and healthier than those who don’t.
Lose excess weight
Obesity itself contributes to the incidence of high blood pressure among several age groups. Obesity can affect the efficacy of hypertensive medications. According to studies, losing extra pounds help control blood pressure (BP) levels.
Obese people with high blood pressure usually suffer obstructive sleep apnea which results in sustained high blood pressure levels. Weight loss can help relieve sleep apnea which in turn reduces blood pressure levels.
Exercise regularly
Engaging in regular physical activity improves your heart health. 150 minutes of exercise a week, or about 30 minutes most days of the week is highly recommended. It can lower your blood pressure by 5 to 8 mmHg.
Having regular exercise helps you lose excess weight and maintain a healthy weight which helps control BP. As you exercise, your blood pressure falls and remains lower afterwards. The longer you exercise, the more your BP falls. Obese men with erectile dysfunction enjoy improved sexual activity when they engage regularly in aerobic exercise.
Examples of aerobic exercises include walking, jogging, dancing, swimming, and cycling. Resistance exercise or strength training, and high-intensity interval training are also beneficial.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol intake has its benefits and can also cause adverse effects. Moderation is the secret. A portion for women and two portions for men daily is considered healthy. Moderate intake of alcohol can lower your blood pressure by 4mmHg and reduce your risks for heart problems, diabetes, stroke, and dementia.
Chronic excessive intake of alcohol increases your blood pressure. It also counters the effect of antihypertensive medications.
Reduce caffeine intake
In some people, caffeine has been found to increase blood pressure levels up to 10mmHg. Research showed that consuming 5 cups of coffee a day (300mg of caffeine) was linked with a 4.8/3.0mmHg increase in 24-hour ambulatory BP. Similar amounts of green or black tea produced a short-lived increase in blood pressure levels.
Reduce stress levels
Exposure to stressful conditions over time may contribute to high blood pressure. Coping strategies such as binge-eating, drinking alcohol or smoking can result in sustained hypertension.
Find out what makes you feel stressed. Once you do, work on reducing or eliminating it. Take time out to relax, engage in pleasurable activities such as hobbies, volunteering and sports. Also, ensure you rest and have enough sleep.
Monitor your blood pressure regularly and keep your appointments
Monitor your blood pressure levels at home. It helps measure how far you have kept your blood pressure within normal ranges. It informs your decisions on what to continue and what to stop doing. It also helps prevent health complications.
Keeping your doctor’s appointment is also important. You can check in with your doctor on what you need to keep doing or what you may need to reduce. You can communicate changes and concerns. Your doctor is also able to make changes in your medications or their doses.